“Hey, Robin, you know, most of our competitors already have a coronavirus claim on their products like us, and I’m not quite sure what can we do to stand out more.”—During the COVID-19 virus outbreak, most disinfectant manufacturers elevate their products’ uniqueness either by reducing the kill time to just mere seconds or to test against more resistant microorganisms such as Human coronavirus 229E. These were like hotcakes! You see it on almost every bottle or product brochure, which is great as we’re cornering the virus! Nowadays, disinfectant manufacturers are interested to level up their products with residual activity or also commonly referred to as ‘long-lasting effect’ against coronavirus.
The existing standard methods for residual activity evaluation can be categorized into 2 groups. Let’s look into them!
Group 1: PAS 2424 and US EPA Protocol # 01-1A
“Hey, Lily, it’s me! Great news! We passed our PAS 2424 test! Now we can claim a bactericidal and yeasticidal residual effect of 24 hours for our product! How awesome is that!”—Group 1 test methods are designed to specifically test the residual bactericidal and/or yeasticidal activity of disinfectants. Check out the table below that summarizes the difference between PAS 2424 and US EPA Protocol #01-1A.
| PAS 2424 | US EPA Protocol #01-1A | |
| Activity Claim | Bactericidal and/or Yeasticidal | Bactericidal |
| Test Microorganism | 1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 15442 2. Escherichia coli ATCC 10536 3. Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 4. Enterococcus hirae ATCC 10541 and/or 5. Candida albicans ATCC 10231 |
1. Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 2. Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 4352 or Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 13048 |
| Number of Abrasion | 3 wet and 3 dry abrasions | 6 wet and 6 dry abrasions |
| Abrasion Method | Manual weighted abrasion | Gardco Washability and Wear Tester |
| Number of Re-inoculation | 5 times | 5 times |
| Obligatory Contact Time | 5 minutes for bacteria, 15 minutes for yeast | 5 minutes |
| Passing Criteria | 3 log reduction (99.9%) | 3 log reduction (99.9%) |
| Claim Residual Time | 24 hours | 24 hours |
Group 2: International Standards Evaluating Efficacy of Biocide-Coated Materials
“Marshall, I just got a call from TECOLAB—they said they could test our plastic tumblers according to a standard called ISO 22196 for bacteria. Let’s give a go to up our tumbler sales maybe?”—Group 2 standard methods such as ISO 22196 and ISO 21702 are international standards that evaluates the efficacy of biocide-coated materials such as plastics against bacteria and viruses, respectively. It’s amazing how these antimicrobial plastics can be found in hospitals on medical devices or even a water bottle!
In brief, the antimicrobial plastic will be exposed to the microorganisms for 24 hours under a humid condition. After the 24-hour contact time, the contaminated surface will be neutralized to quench the antimicrobial activity of the plastic. In order to know how well the antimicrobial surfaces worked, usually the microorganism growth result from the test surfaces are much lower when compared to a control (non-antimicrobial) surface. If you would like to know more in-depth of these method, visit our page here!
“Can We Test for A 24-Hour Protection Effect Towards Coronavirus?”
We’ve been wondering the same too!—To date, there are no specific standard test methods to test the residual virucidal activity and a residual effect longer than 24 hours. However, international disinfectant regulatory authorities such as the National Environment Agency (NEA) of Singapore, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) of Australia, and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of the United States have published suitable guidelines to regulate products that claim for residual virucidal activity for registration purposes.
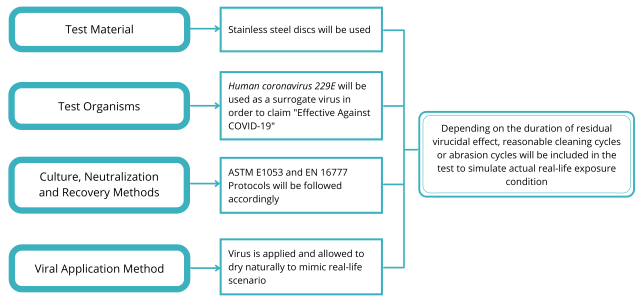
After extensive reviewing of these guidelines, our team got themselves to the drawing board to develop an in-house test method based on published standards. The in-house test method was designed to fulfill the requirements requested by different regulatory authorities. We’ve developed the test method based on PAS 2424, ASTM E1053, and EN 16777. Have a look at the brief protocol below to know more!
Passing Criteria According to Different Regulatory Authorities
“Hey, Moe! By any chance would you know if a 90% reduction against coronavirus is accepted by the regulatory authorities here?”—We noticed a similar effectiveness pattern between the international regulatory guidelines. Most of them would require a 99.9% (3 log reduction) residual virucidal activity for products claiming residual performance against virus. Wondering what are some specific international regulatory needs?
The National Environment Agency (NEA)
The NEA of Singapore has published a guide to evaluate the antiviral efficacy of biocide-coated products. These are categorized into three classes as described in the table below. Which class would you like your product to belong to?
| Contact Time | |||
| Virus Titre Reduction | 0 min to 15 mins | 15 mins to 2 hours | 2 hours to 24 hours |
| > 99.9% (> 3 lg) | Class A | Class B | Class C |
| >99% to 99.9% (> 2 lg but, < 3 lg) | Class A | Class C | Class C |
| 90% to 99% (1 lg to 2 lg) | Class B | Class C | Not ideal for use |
| <90% (< 1 lg) | Not ideal for use | Not ideal for use | Not ideal for use |
| Class A: High traffic volume high prevalence Class B: Medium traffic volume and medium prevalence Class C: Low traffic volume and low prevalence |
|||
The table above is extracted from The National Environment Agency (NEA) Technical Guidance on the Testing of Self-Disinfecting Surface Coatings against SARS-CoV-2
Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)
According to the latest Therapeutic Goods Administration guidelines in December 2021, a disinfectant must produce a 99.9% reduction of virus with a residual activity claim period of no more than 30 days. The recommended standard for residual virucidal activity claims would be a modified ASTM E1053 that includes abrasion and re-inoculation of virus.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
Generally, EPA would consider any methods or studies that are scientifically sound that supports residual antimicrobial activity claims. EPA recommends modifying US EPA Protocol #01-1A and ASTM E1053 for residual virucidal activity claims. As compared to the NEA and TGA, EPA has set more specific performance standards for a 24-hour residual disinfectant. Which criteria do you think stands out from the other regulations?
| Performance Criteria | Residual Disinfectant |
| Meets EPA’s standard for disinfection efficacy | Yes |
| Duration of residual claim | ≤ 24 hours |
| Durability assessment | Abrasion |
| Performance standard for residual bactericidal activity claim | 99.999% reduction |
| Performance standard for residual virucidal activity claim (May only be added for product after obtaining residual bactericidal activity claim) |
99.9% reduction |
| Time to meet performance standard | ≤ 10 minutes |
The table above is extracted from The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Interim Guidance – Review for Products Adding Residual Efficacy Claims
How Can TECOLAB Assist You In Your Residual Activity Claim Journey?
TECOLAB is committed to assist disinfectant manufacturers in achieving high-demand product claims for their disinfectants. Our team customizes and design suitable test methods that suits manufacturer needs, product application, and antimicrobial claim of interest. Disinfectant manufacturers may submit our test protocols to the regulatory authorities such as NEA, TGA, and EPA for approval prior to proceeding with testing. Contact us here if you would like us to get started on designing your customized test protocol!

