Previously we had discussed on the European Standards for disinfectant efficacy in the food, industrial, domestic, and institutional areas. This time around, we would like to introduce the final area: the veterinary area. The use of disinfectants in the veterinary area are not only subjected to professionals but also the public who have taken an interest in farming, outdoor activities that involves animal interactions, and more. Find out more about the need of disinfectants in the veterinary area with a quick read below.
The Veterinary Area – What Do You Need to Know?

A typical farm operation routine would include milking, feeding, animal care and handling, transportation, and the use of processing equipment. In the veterinary area, chemical disinfectants and antiseptics are commonly used in routine farm operations and in veterinary medicine. Disinfectants are essential to reduce the spread of harmful bacteria and viruses amongst animals or between animals and humans, an event commonly described as zoonoses. An example of the good use of disinfectants would be in the milking process. The removal of bacteria during pre- and post-milking by disinfecting the milking vacuum or additional equipment/vehicles can lower the occurrence and spread of intramammary infections (IMIs). Moreover, it is also important to remember that different areas of disinfection requires suitable disinfectants.
intramammary infections (IMIs). Moreover, it is also important to remember that different areas of disinfection requires suitable disinfectants.
There are multiple factors to be considered when selecting disinfectants in the veterinary area. Rough surfaces and high organic soiling are amongst the strong factors that may reduce the efficacy of disinfectants. Other than the reducing microorganism load, the efficacy of disinfectants are also dependent on the surface exposure of these disinfectants. Some disinfectants are tested against porous and non-porous surfaces under different European Standards due to its adaptability to real-life applications. Although a surface may look clean, porous surfaces may still harbor harmful germs, allowing them to fall deep into the material or surface.
Up until now, many good attempts have been made to evaluate the efficacy of chemical disinfectants against microorganisms. This includes the development of European Standards for the effective control of disinfectants and antiseptics by the technical committee in 1990. In order to claim certain product efficacy and suitable use in the veterinary area, the product shall be tested according to the following tabulated European Standards.
| PRODUCT | SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY | ||||
| BACTERICIDAL | YEASTICIDAL/FUNGICIDAL | VIRUCIDAL | MYCOBACTERICIDAL | SPORICIDAL | |
| General surface disinfectants without mechanical action (Clean and dirty conditions) | EN 1656, EN 14349a & EN 16437b | EN 1657, EN 16438a & **b | EN 14675 & EN 17122a | EN 14204, **a & **b | ** |
| General surface disinfectants with mechanical action (Clean and dirty conditions) | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Teat disinfection | EN 1656 | EN 1657 (yeasticidal) | *** | *** | *** |
| Disinfection of equipment by immersion | EN 1656, EN 14349a & ***b | EN 1657, EN 16438a & ***b | EN 14675, **a & **b | EN 14204, **a & ***b | **a & ***b |
| Hygienic handwash | EN 13727 & EN 1499 | EN 13624 (yeasticidal) | EN 14476 | *** | *** |
| Hygienic handrub | EN 13727 & EN1500 | ||||
| Surgical handwash & handrub | EN 13727 & EN 12791 | ||||
| a For non-porous surfaces b For porous surfaces ** No approved standards but relevant ones may become available in the future *** No intention to develop a test |
|||||
Choose the Right European Standard According to Surface Type
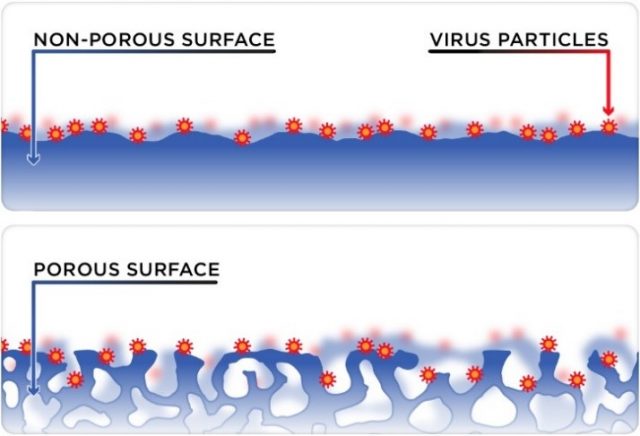
The diagram above illustrates the fate of virus particles when exposed to non-porous and porous surfaces. Photo courtesy of Australian Academy of Science.
Porous Surfaces
“What are porous surfaces?” – Porous surfaces are surfaces that generally absorbs water and moisture. Due to its physical characteristics, porous surfaces are harder to disinfect when compared to non-porous surfaces. In the veterinary area, poultry pens are usually built with wood. This wooden surface has uneven, cracked pores which allows harmful bacteria and viruses to seep through these openings and harbour on the surface. Choosing the disinfectant adapted to these unique surface features will lead to an effective prevention and microorganism transmission. EN 16437 is a European Standard that evaluates the efficacy of disinfectants against bacteria on porous surfaces. In this test, poplar wood is used to mimic actual wood surfaces found around us.
Non-Porous Surfaces
“Ideal for non-porous surfaces.” – A statement found on disinfectants that are proven to be effective against microorganisms on non-porous surfaces. The term ‘non-porous’ reflects liquid or air that are unable to penetrate, thus remaining on the surface. Examples of non-porous materials include glass, metal, plastic, and varnished wood. It is important to note that despite being easier to disinfect, non-porous surfaces are a common source of bacterial transmission. In veterinary medicine, disinfection is usually done on operation tables or equipment that come in contact with the animals. Each veterinary disinfectants has specific properties and benefits. Some can rapidly kill a wide range of harmful bacteria or viruses yet corrode the surface of a treatment table. Therefore, consumers shall elucidate the product application, contact time, and perhaps material compatibility as well. The test method used to evaluate the efficacy of chemical disinfectants against bacteria on non-porous surfaces is EN 14349. In this test, metal discs are used to represent an actual instrument or carrier of microorganism.
Are you wondering if your disinfectant or a particular disinfectant is effective during application? Let us know about it here. TECOLAB provides disinfectant efficacy testing according to the requirements and guideline of the veterinary area European Standards. Do not hesitate to contact us for more info!
Reference:
1. Fitzpatrick, S., Garvey, M., & Gleeson, D. (2018). A review of test protocols for the evaluation of teat disinfectants. International Journal of Dairy Technology, 71(3), 553–563.
2. Ahveninen, A. (2021). How germs spread from surfaces. Retrieved from https://www.science.org.au/curious/people-medicine/how-germs-spread-surfaces
3. EN 14885:2022

